
Mileage is improved due to the water-blown, foamed adhesive process.

Figure 1. Liquamelt Process Overview
Adhesives manufacturers have approached this issue by modifying chemical structures and additives, while equipment manufacturers have sought to reduce consumption with complex stitching, swirl patterns, and foaming devices. To circumvent the challenges associated with hot-melt technology, cool-on-delivery/hot-on-demand Liquamelt® technology aims to create greener alternatives in packaging adhesive technology. It targets a > 70% reduction of the carbon footprint while maintaining the same or better performance characteristics by combining:
- Improved mileage obtained as a result of a water-blown, foamed adhesive process
- An adhesive formulation manufactured with greater than 40% renewable raw materials
- Delivery-point processing

The Adhesive Mechanism
When Liquamelt was first commercially introduced in 2008, it offered customers a different method for packaging adhesives delivery: processing adhesive on demand, as required by the application. This technology produced a safe, room-temperature liquid that could replace traditional hot-melt delivery methods (which require extensive equipment, tanks, and hoses in order to heat large quantities of adhesive and maintain proper temperature). Instead of processing chemicals in large factories, shipping the solid pellets and remelting them, the TurboActivator™ serves as a “mini-factory” for processing the Liquamelt at the delivery point-where it is activated to form the working adhesive. See Figure 1.Meeting the adhesives and sealants industry’s goals of safety, convenience, and efficiency required the development of an adhesive with properties that allowed it to be a stable liquid at room temperature and rapidly transform into a thermoplastic on demand. Based on these criteria, this technology would ultimately require three essential components:
- A liquid carrier component compatible with the adhesive system
- A sponge component to soak up the liquid carrier when activated
- A backbone component capable of creating superior structural integrity and adhesion
The bonding mechanism in the Liquamelt system, which is used as the piece moves out of the compression stage, is very different from either hot melt or cold glue. Instead of sacrificing liquid in the bonding process (which is followed by subsequent crystallization), the parts are initially held together through viscoelastic forces, which then set up in a matter of seconds. Products held together out of the compression stage will gain strength and reliability over time as these bonds relax in fluctuations of temperature and humidity, thus virtually eliminating environmental pop-open problems that are experienced by other thermoplastic systems.

Increasing the Green Factor
In addition to providing a 50% reduction in adhesive consumption, Liquamelt also replaces more than 40% of the raw materials with vegetable oils, reduces overall energy consumption, and minimizes handling costs. The result is a step-change improvement in the carbon footprint, producing a reduction of greater than 70%.Adhesive reduction is brought about by the use of foamed adhesives. The surface area covered by the adhesive bonding the two materials is generally proportional to the load-bearing properties of the assembled part. The most effective means of creating the greatest surface area is to develop a simple foamed adhesive system. This goal can be achieved by capitalizing on the properties of cool-on-delivery technology, which allows the Liquamelt to be formulated with an environmentally friendly blowing agent (i.e., water) and combined with hot-on-demand delivery (i.e., TurboActivator) to simultaneously activate the blowing agent and adhesive. The combination of these technologies provides a low-density, high-surface-area adhesive at the point of application, resulting in an adhesive system capable of expanding up to 10 times its original volume, thus reducing adhesive consumption by half in a variety of sealing applications.
The three components-liquid carrier, sponge and backbone-were evaluated for initial substitution with renewable raw materials. Since the liquid carrier was the largest component by percentage of weight, it was targeted as the first component to be converted. What was once based on petroleum-derived mineral oils could be converted to vegetable oil liquid carriers. This results in an adhesive that now comprises more than 40% sustainable materials.
Less packaging means easier transport. The cool-on-delivery technology allows the material to be transferred in 5-gal bag-in-box systems, drums and/or totes. The reduction of adhesive consumption obtained in the foaming process translates into environmental and cost benefits such as less packaging; lower weights for transport; and less handling, since a 50% increase in mileage means that 50% less material exists at each stage of the process.
Using this technology, energy consumption is reduced on multiple levels. Instead of converting chemicals to hot melts in energy-intensive manufacturing scenarios, transporting twice as much material to the customers, and remelting the pellets for dispensing, Liquamelt can be delivered, processed, and dispensed on demand, saving energy at each step. Depending on the customer’s operating protocol, the cool-on-delivery/hot-on-demand technology reduces the amount of energy consumed by more than 70% while eliminating the moving parts, heated tanks, and hoses needed in traditional hot-melt technology.
The TurboActivator simultaneously serves as a high-efficiency heat exchanger and static mixer. It is enclosed in three layers of insulation, and its thermal cartridge heater is located in the center of the device. In this way, all of the energy transfers efficiently to the activation of the adhesive, producing energy savings from the point of manufacturing to the point of application. In addition, cool-on-delivery adhesives are capable of starting up in 3-10 minutes (vs. 30-60 minutes required by a hot-melt system). Moreover, the system’s ability to hibernate when inactive, as well as its low-energy delivery systems, provides additional savings in energy, depending on the mode of operation (see Figure 2).
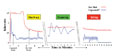
Figure 2. Energy Conservation Depends on Operational Stage
Performance Analysis
As in any industry, the challenge of creating greener packaging adhesives is to create alternatives that are not only environmentally sustainable but also capable of meeting the industry’s high standards. In the case of Liquamelt, the cool-on-delivery model is successfully operating in a variety of manual hand gun and highly automated systems. Because it is applied as a foam, zero- or reduced-cavity modules are generally the dispensing technology used for automatic systems.These liquid bulk feed systems eliminate the need for vacuum systems and can be located remotely, thus reducing the need for floor space, constant monitoring, and refilling. Liquamelt is delivered at room temperature to the point of application via a standard hydraulic piston pump and hoses. This allows operations to feed multiple dispensing heads on multiple lines from a centralized adhesive source. Each system can be expanded from one to four channels by adding modular temperature controllers and TurboActivators. A four-channel unit is capable of processing 35 lbs per hour, which equates to 70 lbs per hour of hot melt.
Converting hot melt and hot melt/cold glue lines requires only the replacement of existing hot hoses and guns with TurboActivator and gun assemblies. The Liquamelt system can be up and running within 10 minutes of installation. Applications range from point-of-purchase, case and tray systems running at 30-70 units/minute to high-speed carton lines running as fast as 250 cartons/minute. Adhesive weights as low as 0.02 g have been obtained with a throughput capacity of 5-7 lbs per hour per channel. The use of the foamed adhesive technology has allowed these applications to realize mileage improvements of 30-70%.
With its HMIS rating of H:1 F:0 S:0 and its non-reactive composition, Liquamelt can be cleaned up with soap and water. Operators have discovered that the characteristics of the foamed polymer make post-activation cleanup easier than hot melt or cold glue. Instead of scraping or scrubbing packaging equipment, as is done for conventional lines, extraneous activated adhesive can be blown off with air or vacuumed up because it only adheres to targeted substrates. This feature has been shown to minimize maintenance and optimize line efficiency.
Hot-melt systems are known for their potential to cause burns. Liquamelt only adheres to targeted substrates, making skin contact less hazardous. While it is strongly recommended that the same precautions taken for hot melts are also followed for activated Liquamelt, it has been discovered that serious burns can be avoided by rapidly brushing the adhesive from the contacted skin.
Because the system is an adhesive foam expanded with steam, the latent heat in the bead allows it to have several seconds of open time while having sealing characteristics in tenths of seconds as the bubbles are compressed-releasing and condensing the steam. This characteristic has led to unusual application characteristics where the typical open time and bond time paradigms are broken, enabling Liquamelt to penetrate plastic and foam applications that often require more complex pressure-sensitive adhesives with elaborate swirl patterns to avoid melting the substrate foam and/or plastics. Figure 3 illustrates applications of the technology.
The three-component adhesive system leads to a polymer structure that behaves like more advanced polymers, creating very strong bonds capable of withstanding temperature latitudes ranging from -40-140°F. This allows customers to use a single adhesive for products that will experience both high- and low-temperature environments.

Figure 3. Potential Applications
A Green Future
Despite hot melts’ stronghold on the packaging adhesive market, the outlook for alternatives such as cool-on-delivery/hot-on-demand adhesives is bright. Driving the demand for greener packaging adhesives are end users’ needs for reduced costs, greater efficiency and optimum sustainability.For additional information, contact Liquid Polymer at 1909 N. Ridge Rd., East Lorain, OH 44055; (440) 277-5100; e-mail info@liquamelt.com; or visit www.liquamelt.com.


