For 40,000 years, people have been using coatings for decoration, protection and camouflage in daily life routines. Early paints contained naturally occurring dyes and used egg yolks, linseed oil, waxes, or other natural binders to help them adhere to surfaces. Many changes have been made to these early formulations, but the industry was truly revolutionized after World War II, when toxic components, such as lead and mercury, began to be removed.
Today, synthetic polymers, resins and solvents are used for coating production. These materials outperform their historic predecessors, showing an increased resiliency for weathering effects such as acid exposure, extreme heating and cooling, and water exposure from rain or snow.
Testing Methods
High-quality coatings are made from high-quality materials, and manufacturers need to test materials to ensure that consumers will be happy with the products they purchase. To ensure that they have the right blend of components, a manufacturer will run loss on drying assays, which examine the amount of material that will volatilize once heated.
ASTM International has dedicated method D 2369 for determining volatile content of coatings using an oven method testing. First approved in 1965, this method effectively determines the volatile content, but does not take advantage of new technology that reduces testing and throughput times, which would allow manufacturers to improve the efficiency of their metrology process and reduce product manufacturing times. In addition, this method is unable to provide real-time results for analysis, which would be helpful to immediately diagnose possible manufacturing problems.
Because of technological advancement in traditional loss-on-drying techniques, ASTM International adopted method D 7232 in 2006. This method is designed to produce the same result obtained from testing using method D 2369, but reduces the testing time from two or more hours to minutes. A loss-on-drying moisture and solids analyzer can provide in situ measurements, giving metrologists the ability to diagnose manufacturing problems immediately.
Testing and Results
For this experiment, three different materials were tested using ASTM method D 2369 and D 7232. For method D 2369, a convection oven was used, and for D 7232 a loss-on-drying moisture and solids analyzer instrument was used. Between sample tests using the analyzer, the coatings and pigment were shaken in their containers. A flat pan with paper was used for each test, and the materials were placed onto the pan using a 5-ml plastic syringe.
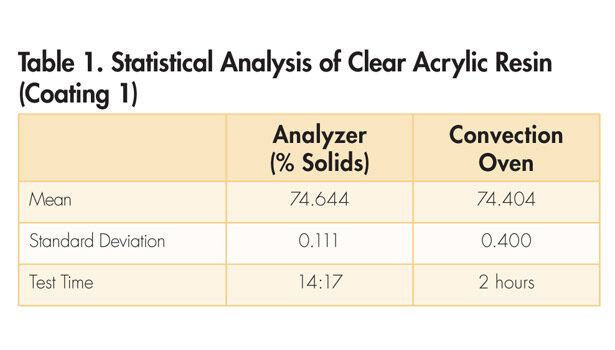
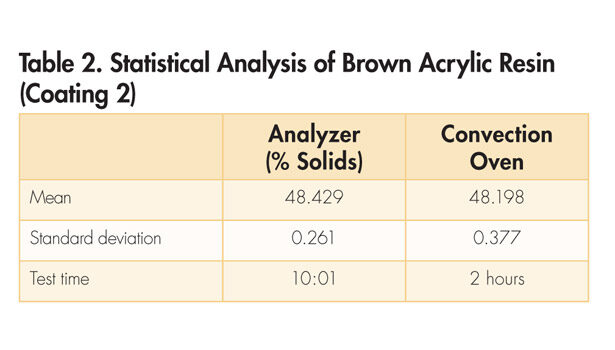
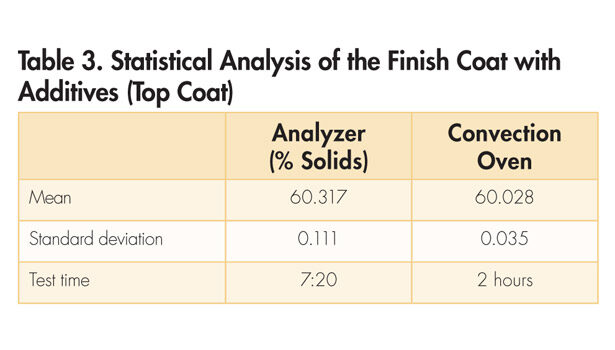
The data from Tables 1-3 show that the two methods provide similar results. In addition, the analyzer showed a significantly tighter testing result range for two of the three sets of testing.
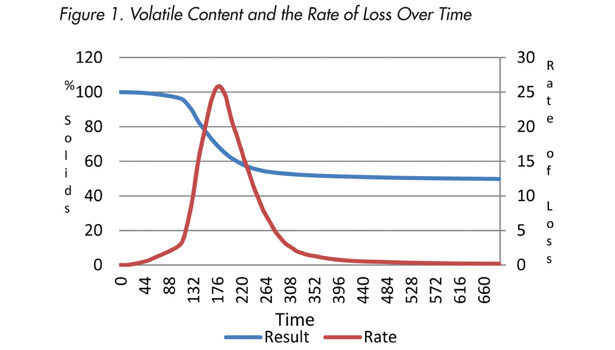
Figure 1 shows that the resin begins to volatilize around 100 seconds, suggesting that the idle temperature is cool enough to prevent the material from evaporating prior to data collection. In addition, the tail of the rate graph shows that the material has lost all volatile content, and the test is allowed to end. This is a typical graph for all three materials that were examined.
More Effective Testing
For testing coatings, rapid loss-on-drying methods prove to be more desirable than traditional testing methods. Both testing methods were able to provide similar results, but the analyzer was able to reduce testing times when compared to the convection oven, and gave a complete profile of the materials as they are being analyzed. This technology can be used to reduce manufacturing throughput times and quality improvement with more information should formulation problems arise.
For more information, visit www.azic.com.