Elastic Structural Adhesives by Hybrid Technology
An adhesive, by traditional definition such as DIN-EN 16920, "is a non-metallic cement which bonds materials by surface adhesion in such a way that the bond exhibits a sufficient inner strength (cohesion)." In modern engineering, this definition is not sufficient in that the bond line is recognized to be an integral part of the body it helps to assemble. Apart from the obvious properties - adhesion and cohesion - the dynamic mechanical parameters such as modulus of elasticity and other viscoelastic properties play an important role in determining the overall mechanical behavior of the body. Such functional bond lines, when properly engineered, can be instrumental in absorbing vibrational or static stress. The latter is typical in situations where two materials of different thermal expansion coefficients are joined.
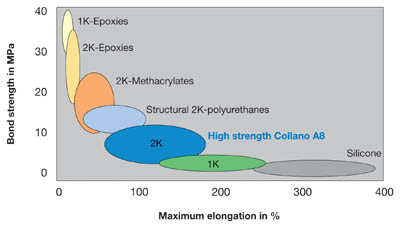
It is well known that there is a clear correlation between the chemical nature of the backbone polymer of the adhesive and the properties of the bond. Polymers with a rigid chemical structure and a high degree of crosslinking yield high bond strengths and high moduli. In other words, they are tough but brittle. Epoxies are typical representatives of such adhesive materials. At the other extreme are polymers, which form flexible networks. They are highly elastic, i.e., they exhibit low elastic moduli and limited bond strengths. Various siloxane compounds fall into this class.

Polymer Alloys for Elastic Structural Adhesives
The intermediate regime, i.e., structural bonds with yet a high degree of elasticity, can be covered with hybrid formulations. These are polymer alloys consisting of a matrix of silyl-reactive polymers (elastic phase), which host domains of epoxy-reactive polymers (hard domains). With a diligent choice of components, mixing ratio and the size of respective domains, the overall properties of the bond line can, to a high degree, be tailored for the purpose.Figure 1 represents a microscopic view by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of such a polymer alloy. The dark domains stem from the epoxy phase and have a diameter of less than 0.5 microns.
By means of a diligent choice of the individual components (i.e., backbone polymers, fillers and blending conditions), a substantial range of elasticity, bond strength and adhesion profile can be spanned. This allows for structural bonding of a variety of surfaces, including glass, metals, wood and many other materials employed in the automotive and transport industry. By means of additives, additional functionalities such as corrosion protection or flame retardency can be added.

Examples of Elastic Structural Bonds
The versatility of these systems can be demonstrated with the following examples. For structural glazing, the formulation can be chosen such as to yield a completely transparent bond line. Thereby the loft character of the material glass is not perturbed by the assembling medium. UV stability is achieved both by the choice of suitable backbone polymers and UV stabilizing additives.A completely different objective is pursued in the example of containers, which host the electronic equipment for railway tunnels. Here the mechanical and flame retardant properties were of paramount importance.



Application and Curing
Two-component epoxy/silane adhesives are applied by means of a static mixer in which the individual components are blended immediately prior to application. For small-scale applications, twin chamber cartridges are used. For medium lot sizes, a hand-held applicator with automatic metering of the two components (see Figure 6) will be the most efficient way, whereas robots are employed in automated assembly lines.Summary
Alloys of epoxy and silane reactive polymers allow for the formulation of elastic structural adhesives. The mechanical dynamic properties of such adhesives can be engineered to the needs of the application. The bond lines of such systems are suitable to absorb static or vibrational stress. With the help of additives and fillers, a great manifold of properties can be introduced.For more information, contact Dr. Damien Ferrand at damien.ferrand@collano.com or Dr. Willi Schwotzer at willi.schwotzer@collano.com ; or visit http://www.collano.com .
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!




