Influence of Rheology on Mixing Behavior in Static Mixers
The second of a series on static mixing, this article focuses on how the rheology of a material impacts mixing behavior.
Adhesives are currently becoming increasingly important in a wide variety of applications in the dental, industrial, and health care industries. Two-component adhesives are being used more and more because of their unique properties, and static mixers are the most frequent choice for mixing the two-component material before application.
When selecting the optimum static mixer, the rheological properties of the starting components and their mixing ratio play an important role. In particular, highly viscous materials with a high proportion of fillers often have a pronounced non-Newtonian behavior. Therefore, a good understanding of the rheological behavior of the components to be mixed is important.
Basics of Rheology
A classification of the different material properties can be found in the Table 1.
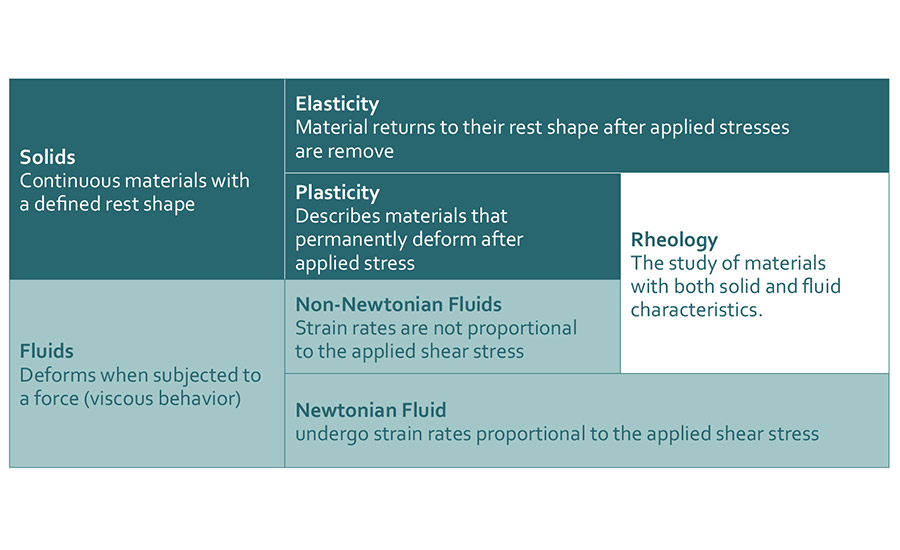
For Newtonian fluids, viscosity is independent of load. This means that the viscosity depends on the temperature, but not on the shear stress. Only a small group of mostly low-viscous fluids (such as water, milk, salad oil) exhibit such constant viscosity. For most fluids, the viscosity changes under shear stress; these are called non-Newtonian fluids.
Non-Newtonian fluids can exhibit shear-thinning (structurally viscous) or shear-thickening (dilatant) flow behavior. Shear-thinning flow behavior is characterized by a decrease in viscosity with increasing shear rate. Typical materials exhibiting this behavior are coatings, adhesives, polymer solutions, and polymer melts. Shear thickening means that viscosity increases with increasing shear rate. Materials that typically exhibit such behavior include highly filled dispersions, such as ceramic suspensions, starch dispersions, sometimes dental fillings (dental composites), and special composites for protective clothing.
Since non-Newtonian fluids are shear dependent, measured viscosities should always be reported together with the exact shear conditions and, in the best case, as a function of shear rate. Often, the viscosity can be approximated section-wise by a power law.
A material is called viscoelastic if it shows a mixture of viscous and elastic behavior. Plasticity is the behavior if a material that behaves as a solid under low applied stresses starts to flow above a certain level of stress, called yield stress
Often, the viscosity is not only a function of the shear rate, but additionally also time-dependent. If such materials are exposed to shear stresses, they do not change their viscosity instantly, but over time. As time-dependent shear-thinning materials are called thixotropic, shear-thickening materials are called rheopectic.
In addition to the rheological behavior, the viscosity of a material is also strongly dependent on temperature. Generally, in the case of liquids the viscosity decreases with increasing temperature. This can have a strong impact. For example, the viscosity of a typical engine oil decreases by a factor of three when the temperature is increased from 23 °C to 50 °C.
Impact of Rheological Properties on the Performance of Static Mixers
The optimal achievable mixing quality depends on the type of mixer, the number of mixing elements, the mixing ratio, and the viscosity ratio of the two components. A pre-defined mixer generally achieves the best mixing quality when materials with a mixing ratio of 1 to 1 and the same viscosity are mixed.
In many cases, however, this optimum condition does not exist and a rather high-viscous, shear-thinning resin is to be mixed with a rather low-viscous Newtonian curing agent. Since optimum mixing occurs at equal viscosity, it is advantageous to select a mixer that mixes at a shear rate that results in equal viscosities of the two components.
However, the rheological behavior of the material not only influences the mixing quality, but in particular also the pressure loss in the mixer. If, for example, a high-viscous material is to be discharged with a high volume flow, the resulting high pressure loss in the mixing element leads to high mechanical loads on the cartridge and the mixer housing. These loads can have a negative impact on functionality (pre-flow of one component, blow-up of the cartridge or mixer housing) or ultimately even damage the plastic parts.
In such a case, it is advisable to choose a mixer with a bigger diameter, which reduces the pressure loss significantly.
Material Guideline to Achieve Good Mixing Results
It is advantageous if material manufacturers, together with the mixer manufacturer, ensure the easy mixability of new materials and components already in the formulation phase. At this stage, it is even possible to design a customized mixer for such an application. Even if an exclusive solution is not desired, good mixability of the components can be ensured in advance, which then leads later on to shorter mixers with fewer mixing elements and lower pressure loss.
From a rheological point of view, good mixability is achieved by observing the following guidelines:
- Both components should have a similar rheological behavior. Similar rheological behavior means that the viscosity over shear strain rate curves run in a log/log diagram in parallel and very close to each other. In such a case it is guaranteed that in a wide range of operating conditions, similar mixing quality can be achieved.
- The volumetric mixing ratio of both components should be close to one. Application tests with material with a high volumetric mixing ratio yield a much higher number of mixing elements necessary to reach an adequate mixing quality.
- Due to the shear thinning behavior of many materials, the actual viscosity of the material in the mixer is lower than specified in the data sheet because of the high shear rates in the mixer. Typical shear rates in a static mixer are in the range of 20 > S > 200 1/s. Nonetheless, a too-high actual viscosity should not be exceeded, as this will at best result in the desired volume flow not being achieved. In the worst case, this will lead to a loss of function or mechanical failure.
Special Mixer Geometries for Materials with Challenging Rheology
If for various reasons it is not possible to follow the above formulation guidelines of an easy-to-mix material, medmix® also offers systems to mix materials with challenging rheological behavior:

Blueline System
This system has been specifically designed for applications where a high-viscosity material is to be applied at a high flow rate. From the cartridge, to the mixer, to the mixer tip, the individual parts of the Blueline system have been optimized for the lowest possible pressure drop. This enables the user to discharge even material with a very high actual viscosity at an acceptable flow rate.
X-Grid Mixers
The X-Grid mixer is ideally suited for resin/hardener systems that are difficult to mix — e.g. 2K adhesives, epoxies, polyurethanes, silicones, resins or varnishes — as well as for components with a large viscosity and/or mixing ratio. In addition, the dispersing effect of insoluble materials is significantly higher. Thus, X-Grid technology can be used for low- and medium-viscous materials that are difficult to mix with current static mixing technology. For such materials, the use of X-Grid technology can result in mixers that are significantly shorter than current mixers.
Learn more about medmix at medmix.swiss.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!





.webp?height=200&t=1672175877&width=200)

