Driving Defossilization in the Adhesive Tape Industry
Innovation, regulation, and collaboration are converging to reshape the adhesive tape landscape into a model for low-carbon transformation.

In a world racing toward net-zero, the adhesive tape industry — a seemingly modest player — holds untapped potential to drive meaningful change. From automotive manufacturing to electronics and packaging, tapes are integral to modern production, yet their carbon footprint often goes unnoticed. As sustainability climbs up the agenda, industry leaders are turning their focus to reducing Scope 3 emissions, sourcing low-carbon raw materials, and embracing circular design principles. Let's take a look at how innovation, regulation, and collaboration are converging to reshape the adhesive tape landscape into a model for low-carbon transformation.
Tackling Raw Materials for Defossilization
One of the first steps in driving defossilization involves reevaluating the raw materials used in adhesive tapes. Historically, the industry has relied on petrochemical derivatives such as synthetic rubbers, acrylics, and silicone-based adhesives. This dependency directly contributes to the carbon intensity of the products.
Biobased alternatives, including plant-derived polymers made from cellulose, starch, or vegetable oils, are increasingly seen as viable replacements for fossil-based materials. Similarly, recycled raw materials could supplement both adhesives and backing materials, reducing virgin material usage while promoting sustainable sourcing practices.
The tapes industry now offers several commercial products featuring both biobased and recycled content, some of which are summarized below:
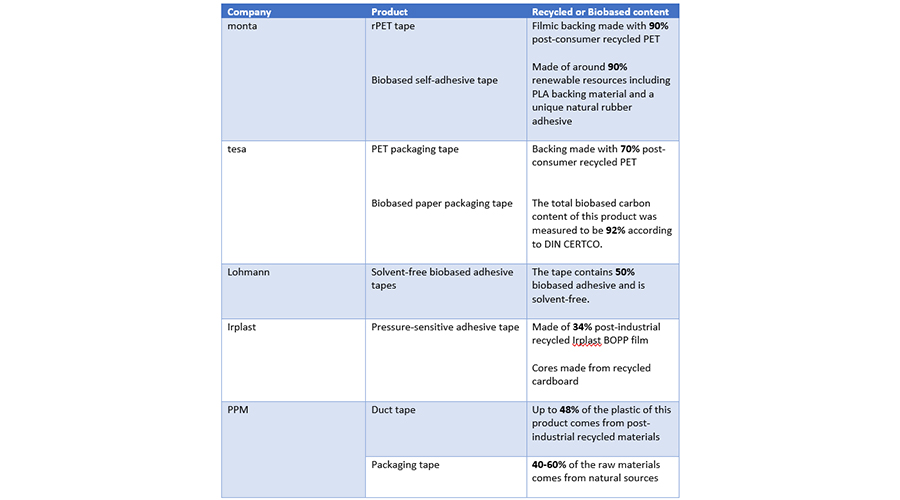
Additionally, supply chain transparency — ensured through digital tracking systems and partnerships with ESG-compliant suppliers — creates a robust foundation for sustainable practices, addressing indirect emissions generated during raw material procurement.
Revolutionizing Manufacturing with Energy Efficiency
Processes such as coating, drying, and curing are central to adhesive tape production. Addressing these processes through energy-efficiency measures and renewable energy integration is essential for defossilization.
Innovative manufacturing practices include the implementation of energy-efficient equipment, optimized production schedules, and the use of heat recovery systems to capture and reuse energy. Moreover, adhesive tape manufacturers can shift to renewable energy sources like solar or wind power to reduce dependence on traditional fossil fuel-based electricity. Investments in on-site renewable energy infrastructure, including solar panel installations, can drastically lower operational emissions. For businesses unable to generate their own clean energy, partnering with utility companies for green energy procurement offers a reliable alternative.
Redefining Product Design for Sustainability
Driving defossilization also necessitates rethinking how adhesive tapes are designed. Reducing material usage, improving product longevity, and incorporating innovative functionalities are key steps in this process.
For instance, lightweight adhesive tape designs with thinner layers can significantly reduce raw material demands. Adhesives incorporating multifunctional properties — such as insulation or flame resistance — enable reductions in additional components, improving both sustainability and performance. Debonding-on-demand technologies exemplify groundbreaking innovation by facilitating clean and controlled disassembly of bonded components for recycling and reuse. This technology encourages alignment with circular economy practices, ensuring the end-of-life disposal of adhesive tapes does not result in excessive material waste.
Fostering Industry Collaboration and Policy Advocacy
Systemic defossilization will require collective efforts across the adhesive tape value chain. Partnerships with research institutions, government agencies, and non-governmental organizations can drive systemic change by fostering innovation and establishing standards.
Raising consumer awareness about the environmental benefits of low-carbon tapes can boost demand and adoption. Additionally, clear end-of-life instructions can encourage responsible disposal or recycling. Industry bodies like Afera, The European Adhesive Tape Association play a key role by promoting knowledge-sharing, shaping regulatory responses, and coordinating joint initiatives.
One standout example is that of TACK (Tape and Adhesives Calculation Kit) —the newly launched Product Carbon Footprint (PCF) Calculation Tool for the adhesives and tapes industry, which has been jointly developed by Afera and IVK, the German Adhesives Association.
What gets measured gets managed
For most industries, tackling Scope 3 emissions has long been a challenge. TACK now provides a standardized, user-friendly solution, ensuring businesses can accurately assess and report their PCFs. This web-based tool, designed by Sphera, is backed by ISO standards, TfS guidelines, and third-party verification.

Key Features of TACK:
- Life-cycle assessment (LCA): TACK enables cradle-to-gate PCF calculations with ease and precision, evaluating greenhouse gas emissions across the entire product life cycle.
- Compliance with ISO standards and TfS PCF guidelines: It adheres to standards such as ISO 14067:2018 and ISO 14040:2006 and the Together for Sustainability (TfS) PCF guidelines, which provides comprehensive instructions for calculating cradle-to-gate PCFs for chemical manufacturers, increasing accuracy and standardization.
- Regulatory alignment: TACK prepares manufacturers for evolving European regulations, including the Eco-design for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR), which mandates PCF data for product transparency and environmental compliance.

Applications of TACK:
By offering measurable metrics and supporting informed decision making, TACK serves as a cornerstone for the adhesive tape industry’s transition toward defossilization.
- Identifying emission hotspots: By pinpointing high-emission stages in production or raw material procurement, manufacturers can target areas for improvement.
- Supply chain optimization: Transparent PCF calculations promote collaboration with suppliers to reduce indirect emissions.
- Meeting carbon neutrality targets: Through actionable insights, manufacturers can align their operations with global climate goals, including the European Green Deal’s objective of achieving net-zero emissions by 2050.
Conclusion: Building a Low-Carbon Future
Driving defossilization in the adhesive tape industry is not just a critical step toward addressing global climate change, but also an opportunity for innovation, efficiency, and sustainability. From raw materials to manufacturing, product design, and end-of-life management, each stage of the adhesive tape life cycle offers opportunities to reduce emissions and promote sustainable practices.
The integration of tools like TACK underscores the industry’s commitment to transparency, measurable progress, and environmental accountability. By embedding circular economy principles, fostering collaboration, and embracing advanced technologies, the adhesive tape industry is poised to lead the charge toward a sustainable, low-carbon future.
Let’s build this future together — one bond at a time.
Learn more about Afera at https://afera.com.
Images within the column are provided courtesy of Afera.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!





