Burned No More: Lignin’s Breakout Role in Sustainable Chemicals
Once burned as waste, lignin is gaining value as a renewable replacement for fossil-based feedstocks.

In the drive to decarbonize chemical production, some of the most promising solutions come from unexpected places. Lignin, once largely burned for energy, is now being explored as a valuable input for a wide range of green applications. As the industry looks beyond fossil fuels, lignin is gaining new relevance as a renewable chemical feedstock with untapped potential. At the same time, a diverse array of emerging manufacturing technologies are jostling for position in the race to define the future of sustainable chemical production.
As the chemical industry continues its shift toward sustainability, attention is turning to next-generation feedstocks. These are derived from renewable and waste sources and serve to cut carbon emissions and reduce fossil dependency. A new report from IDTechEx, Next-Generation Feedstocks for Sustainable Chemicals 2025–2035: Markets, Players, Forecasts, focuses on these next-generation feedstocks. The report provides in-depth insight into key technologies, industry trends, and commercial opportunities that will shape the future of green chemical production.
The Benefits of Lignin
The reports stated that among the most promising, yet underutilized, components of these renewable inputs is lignin, an aromatic polymer found in lignocellulosic biomasses, such as wood and agricultural residues. Unlike other biopolymers, cellulose and hemicellulose, which are widely used to produce biobased sugars and chemicals, lignin has long been relegated to low-value uses, chiefly incinerated to generate process heat. According to IDTechEx, approximately 95% of lignin produced globally is burned, with only a small fraction repurposed in applications such as animal feed.
This underutilization represents an opportunity. If lignin can be efficiently extracted in high-quality forms, it has the potential to replace petroleum-derived products in a range of applications that span bitumen replacements for road surfacing to battery anodes and sustainable packaging. New extraction technologies are now unlocking this potential, transforming lignin from a waste by-product into a valuable resource. In this article, IDTechEx explores three of the many innovative extraction technologies featured in its recent report, highlighting the pioneering work of Sonichem, Lixea, and Anellotech.
Ultrasonic Cavitation Unlocking Odor-Free Lignin
UK-based Sonichem is pioneering a low-energy lignin extraction technology using ultrasonic cavitation. This process begins with sawdust, which is dissolved in water to form an aqueous mixture. Ultrasonic waves then generate extremely localized high temperatures and pressures, breaking apart the complex bonds between lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose. A recyclable organic solvent (a carboxylic acid) assists in the separation, and the method operates at relatively low temperatures, enhancing energy efficiency and process safety.
The result? A low molecular weight lignin (approximately 2,000 g/mol), which is odor-free and soluble in organic solvents. At pilot scale, Sonichem is already producing lignin valued at £2,500 per tonne, more than four times the value of biobased sugars. This positions lignin as a strong candidate for specialty applications such as adhesives, coatings, and composites.
With a commercial plant planned in Scotland and first revenues expected by 2027, Sonichem is poised to tap into a feedstock that is abundant, renewable, and underexploited.
Ionic Liquids Driving Low-Energy Wood Fractionation
Sweden-based Lixea has developed the Dendronic® Process, which uses ionic liquids (molten salts that exist as liquids near room temperature) to fractionate lignocellulosic biomass into its three primary components: cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin.
This solvent-based extraction method is notable for its low-temperature and low-energy requirements, thanks to the unique properties of ionic liquids. Unlike traditional processes that rely on volatile or toxic chemicals, ionic liquids derived from the Dendronic Process are non-volatile, non-flammable, and recyclable solvents, offering a safer and more sustainable alternative for biomass processing.
Lixea’s pilot plant in Sweden, commissioned in 2022, has demonstrated the scalability and performance of this technology. In 2025, the company was awarded €21.5 million in funding from the European Council Innovation Fund to further develop and commercialize the process with a first-of-its-kind pre-commercial demonstration plant. The high-quality lignin extracted is being evaluated for use in applications such as thermoplastics, carbon fibers, and construction materials, sectors that are actively seeking sustainable inputs with lower embedded carbon.
One-Step BTX from Biomass via Bio-TCAT
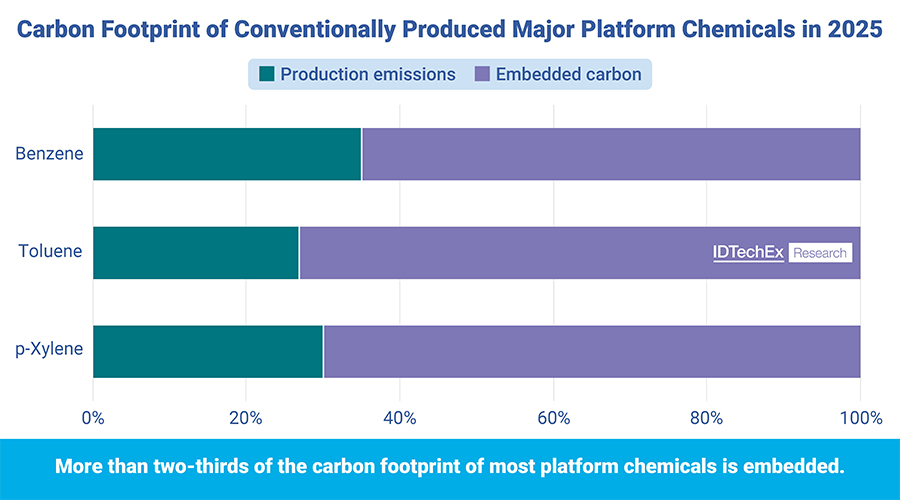
In the United States, Anellotech is advancing the production of biobased BTX (benzene, toluene, xylene), key aromatic compounds. Its proprietary Bio-TCAT® process thermally converts non-food biomass such as pine wood into BTX in a single-step, energy-self-sufficient process.
Utilizing a fluidized bed reactor, the process breaks down the biomass and catalytically reforms it into aromatics. Unlike conventional methods that require hydrogen or multiple processing steps, Bio-TCAT generates its own energy from residual biomass, contributing to a significantly lower carbon footprint and more favorable economics.
Anellotech’s TCat-8 demo plant has proven the technology at scale, and the company is now actively seeking capital investment, partners, and industrial sites to launch its first commercial plant, with full engineering work completed in 2025.
The ability to produce drop-in petrochemical replacements from renewable feedstocks positions Anellotech as a critical enabler of green aromatics, a cornerstone of future sustainable materials and fuels.
A Sustainable Future for Chemicals
These three companies are among many others who are spearheading the shift towards sustainable chemical production. Through innovative extraction techniques that are more efficient, less energy-intensive, and more scalable, they are creating the groundwork for a future where a wide range of chemicals and materials can be produced from next-generation feedstocks.
As detailed in IDTechEx’s report, the market for chemicals derived from next-generation feedstocks is expected to grow at a 16% compound annual growth rate between 2025 and 2035, with lignin playing a central role in replacing fossil-derived aromatics. The report analyzes the technical, economic, and policy factors shaping this landscape, offering strategic insight into the companies, partnerships, and breakthroughs driving progress.
For more information on the report, visit www.IDTechEx.com/NextGenFeedstocks.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!






