Home » Keywords: » structural adhesives
Items Tagged with 'structural adhesives'
ARTICLES
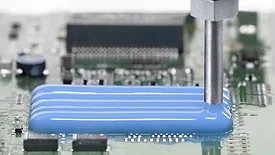
Strengthening the Bond with Structural Adhesives
Two-component, solvent-free epoxy adhesive material provides high adhesion to metallic substrates while also withstanding high movement or cyclic fatigue.
August 18, 2023
Keep the info flowing with our newsletters!
Get the latest industry updates tailored your way.
JOIN TODAY!Copyright ©2026. All Rights Reserved BNP Media.
Design, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing